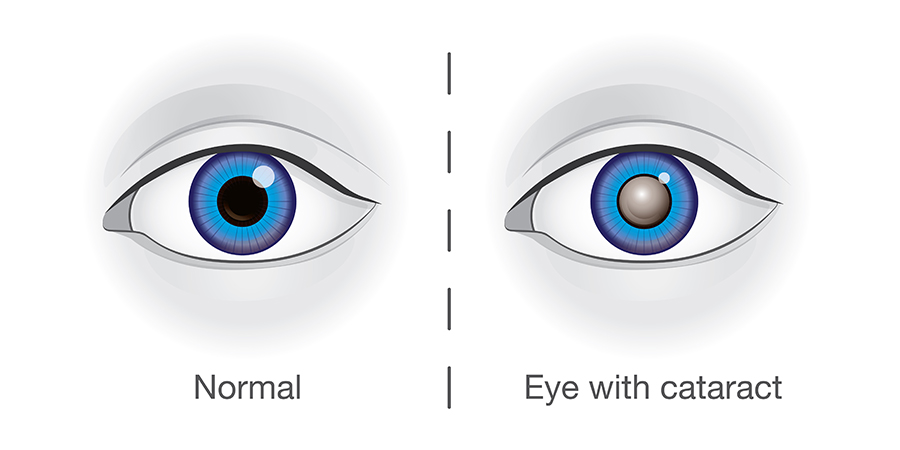
Cataract Overview
A cataract is a cloudy spot in your eye’s lens. As you age, cataracts become more and more common. In actuality, more than half of all Americans 80 years of age and older either have cataracts or have undergone cataract surgery.
You might not be aware that you have a cataract at first. However, cataracts have the potential to dull your vision over time. You could find it challenging to read or perform other common tasks.
The good news is that cataracts can be removed surgically. The safe procedure of cataract surgery fixes any eyesight issues brought on by cataracts.
Symptoms of cataracts
If you have a cataract, you can notice the following changes in your vision:
- The vision that is hazy
- Cataract that causes double or ghostly vision in the eye
- Extra sensitivity to light (especially with oncoming headlights at night)
- Needing additional light to read in the dark or having problems seeing well at night
- Observing vivid hues as faded or yellow-toned
- Inform our best ophthalmologist (at Bharti Eye Foundation) if you have any of these cataract symptoms.
- Images may appear dull or yellow due to cataracts.
- A sign of cataracts is blurry or poor vision.
- Ghostly or distorted pictures may be caused by cataracts.
What are the Causes of Cataracts?
The primary factor is aging. This is brought on by typical eye changes that appear after the age of 40. At that point, the lens’ regular proteins begin to degrade. The cloudiness of the lens is due to this. Lens clouding typically begins in people over the age of 60. However, visual issues may not manifest for several years.
Am I at Risk of cataracts?
As you age, your chance of developing cataracts increases. Furthermore, you face a larger risk if you:
- Have some health issues, such as diabetes
- Smoke
- Overindulge in alcohol
- Have a history of cataracts in your family
- Have you undergone any eye surgery, radiation therapy, or eye injuries on your upper body?
- Have a history of solar exposure
- Utilize steroids (medicines used to treat a variety of health problems, like arthritis and rashes)
Speak with our best eye doctor if you’re concerned that cataracts could be in your future. If there is anything you can do to reduce your risk, inquire.
Types of cataracts
Like an onion, the lens is made up of layers. The capsule is the most exterior. The cortex is the deepest layer of the capsule, and the nucleus is the outermost layer. In any of these places, a cataract could form. Cataracts get their name from where they exist in the lens:
- The lens’s nucleus has a nuclear cataract. With time, the nucleus usually turns from clear to yellow and occasionally brown, darkening with time.
- The cortical layer of the lens, which encircles the nucleus, is affected by a cortical cataract. The cataract has a wedge- or spoke-like appearance.
- The back outer layer of the lens contains a posterior capsular cataract. Frequently, this kind progresses more quickly.
Diagnosis of Cataracts
Our best eye doctor will do a thorough eye exam to evaluate your eyesight and look for cataracts. It will also include a tonometry exam to gauge your eye pressure and an eye chart test to assess your vision at various distances.
The most popular tonometry test flattens your cornea with a painless air puff while measuring your eye pressure. Additionally, our best eye specialist will administer medications to your eyes to enlarge your pupils. This makes checking for damage to the retina and optic nerve at the rear of your eye simpler.
Checking your color perception and glare sensitivity are two other tests that our doctor might run.
What Is the Treatment?
Cataracts may only be removed surgically; however, you may not require it immediately. Early detection of the issue may allow you to get by with a fresh prescription for your glasses. Your vision may temporarily improve with a stronger lens.
Use a magnifying glass or a bulb that is brighter if you are having problems reading. If glare bothers you, consider purchasing specialized glasses with an anti-glare coating. When you drive at night, they can be useful.
Pay close attention to how your cataracts impair your vision. It’s essential to seek help when your vision issues begin to interfere with your everyday activities, especially if they make driving risky — it’s time to talk to your doctor about surgery.
Surgery for cataracts
In all cataract surgeries, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial one. Cataract surgeries come in a variety of forms.
The thought of having surgery on such a delicate area as your eye could make you feel a little uneasy. However, it’s a really widespread practice. To numb your eye, you will be given a drug called a local anesthetic. You won’t feel anything and will be awake but medicated.
You do not need to spend the night in the hospital and it often takes 15 to 20 minutes. When a patient has cataracts in both eyes, their doctor will wait until the first eye has fully recovered before operating on the second.
More than 95% of those who receive this procedure report improved vision thereafter.
- Small-incision surgery. This procedure may also be known as phacoemulsification by our doctor. Your cornea is sliced very slightly by the surgeon. They insert a little device into your eye that emits ultrasound waves, which separate your hazy lens. After that, they remove the parts and insert the artificial lens.
- Big-incision surgery. Although it isn’t done very frequently, doctors will occasionally advise it for bigger cataracts that are causing greater vision problems than typical. Extracapsular cataract extraction is another name for the procedure. Your cloudy lens is completely removed by your surgeon, who replaces it with an artificial one. As opposed to a small-incision operation, this one will likely take you a little longer to recover from.
- Femtosecond laser surgery. During this procedure, your surgeon separates the lens using a laser. The replacement lens will then be inserted, just like with the other varieties. If you also have astigmatism, a corneal curvature that causes your vision to be hazy, your doctor might advise you to try this. By reshaping your cornea with the laser during cataract surgery, our physician can address that issue.
This Article is posted here.